In the realm of nocturnal exploration and surveillance, heat detection binoculars stand as indispensable tools, offering users the ability to peer into darkness and uncover hidden mysteries. However, within this category, two distinct technologies reign supreme: thermal imaging binoculars and night vision binoculars. Understanding the differences between these two can be crucial for selecting the right tool for the job. Let's delve into the nuances of each, shedding light on their unique capabilities and applications.
What Is Thermal Vision Binocular and How It Works?
Thermal vision binoculars, also known as thermal imaging binoculars, are specialized optical devices equipped with thermal imaging technology. Unlike traditional binoculars, which rely on visible light, thermal vision binoculars detect infrared radiation emitted by objects due to their temperature. Thermal technology in heat detection binoculars operates on the principle of capturing infrared radiation emitted by objects. This infrared radiation, also known as heat signatures, is a form of electromagnetic radiation emitted by all objects with a temperature above absolute zero. Thermal binoculars employ specialized sensors capable of detecting and converting this infrared radiation into visible images. This allows users to see heat signatures, even in complete darkness or adverse weather conditions where visibility is limited.
How Thermal Vision Binoculars Work
Detection of Infrared Radiation: Thermal vision binoculars are equipped with microbolometer sensors that are highly sensitive to infrared radiation. When an object emits infrared energy, the microbolometer sensors detect these heat signatures.
Conversion into Visible Images: The detected infrared radiation is converted into electronic signals by the microbolometer sensors. These signals are then processed by the binoculars' onboard electronics to generate a thermal image.
Displaying Thermal Images: The thermal image generated by the binoculars is displayed on the viewing screen, typically using a color palette to represent different temperature ranges. Warmer objects appear as brighter colors, while cooler objects appear as darker colors.

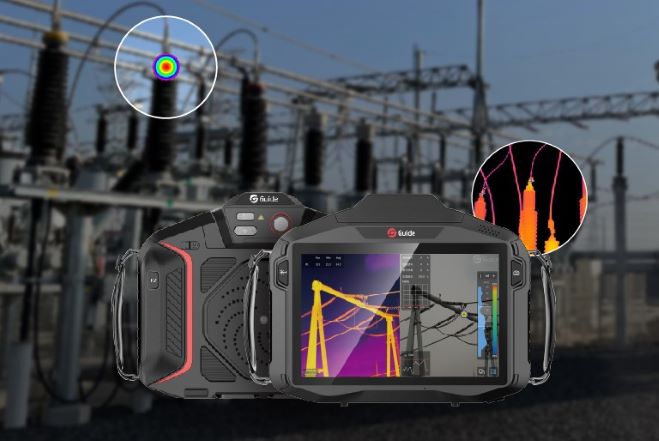
Guide TN Normae Series Thermal Vision Binoculars: Classic Design for Enhanced Comfort and Advanced Functionality
As an expert in heat detection binocular, Guide Sensmart Tech launched TN series. The TN Normae Series Thermal Vision Binoculars are designed with a classic binocular form factor, prioritizing user comfort during extended observation sessions. Their ergonomic design and balanced weight distribution reduce fatigue, ensuring a comfortable experience even during prolonged use.
Equipped with a high-sensitivity VOx uncooled IR detector, these binoculars deliver top-tier imaging quality. Experience detailed thermal imaging and immerse yourself in the observation with the full-color OLED 1024×768 high-definition display.
With a multitude of functions, the TN Normae Series is versatile enough to meet all your needs. Whether it's capturing photos or videos, connecting via WIFI, utilizing laser ranging, or accessing GPS and compass features, these binoculars have you covered.

What Is Night Vision Binocular and How It Works?
Night vision binoculars are advanced optical devices designed to enhance visibility in low-light or nighttime conditions. These binoculars utilize sophisticated technology to amplify existing ambient light, including moonlight, starlight, or artificial light, and provide clear, magnified images. By intensifying available light, night vision binoculars enable users to see in the dark, revealing details that would otherwise remain hidden to the naked eye. They are widely used in activities such as wildlife observation, surveillance, navigation, and law enforcement, offering enhanced situational awareness and operational effectiveness in nocturnal environments.
How Night Vision Binoculars Work
Objective Lens: At the forefront of night vision binoculars lies the objective lens, tasked with gathering ambient light from the surrounding environment. This gathered light forms the foundation upon which the entire night vision process unfolds.
Photocathode: Once the ambient light passes through the objective lens, it encounters the photocathode—a crucial component within the binoculars. The photocathode's role is to convert incoming photons (particles of light) into electrons, initiating the transformation of light energy into an electronic signal.
Microchannel Plate (MCP): As the electrons generated by the photocathode traverse the interior of the night vision binoculars, they encounter the microchannel plate—a finely crafted array of microscopic channels. Here, a phenomenon known as electron multiplication occurs, rapidly amplifying the number of electrons and intensifying the electronic signal.
Phosphor Screen: The intensified electronic signal reaches its culmination at the phosphor screen—a luminescent surface within the binoculars. Upon striking the phosphor screen, the intensified electrons release photons, generating a visible image that faithfully represents the original scene. This process produces the characteristic green-tinted imagery commonly associated with night vision devices.
Guide DN Series Handheld Digital Vision Binoculars
For heat sensor night vision binoculars, Guide Sensmart Tech has DN Handheld Digital Series. The Guide DN Series Handheld Digital Vision Binoculars, exemplified by the DN30 model, represent a paradigm shift in nighttime visibility and surveillance.
With its state-of-the-art 3840x2160@2μm moonlight low-light CMOS sensor and 1920x1080 AMOLED display, the DN30 delivers breathtaking 4K ultra-high-definition visuals that captivate the senses, both day and night. Whether navigating through moonlit landscapes or surveilling under the cloak of darkness, these binoculars offer unparalleled clarity and detail, providing users with a truly immersive viewing experience.

With their cutting-edge technology, ultra-high-definition visuals, and innovative features such as the infrared fill light, these binoculars empower users to unlock the secrets of the night with unparalleled clarity and precision. Whether for wildlife observation, security operations, or outdoor exploration, the DN30 Handheld Digital Binoculars are the ultimate companion for navigating and illuminating the darkness.

Difference Between Night Vision and Thermal Imaging
Night vision relies on nearby visible light for operation, while thermal imaging functions without the need for any light source.
Night vision amplifies visible light in the immediate vicinity, while thermal imaging utilizes infrared sensors to detect temperature disparities among objects within its field of view.
Night vision enhances the brightness of a scene and renders it in green-tinted images, while thermal imaging translates heat signatures into clear, visible images, with objects exhibiting higher temperatures depicted in bright yellow, orange, or red hues.
Adverse conditions like dust, smoke, overcast skies, rain, and fog can impede night vision, yet have no impact on thermal imaging, which can operate in complete darkness.
Night vision, though considered outdated, is less expensive but offers lower quality compared to alternative technologies. Conversely, thermal imaging is highly sought after for its ability to effectively enhance nighttime safety, surpassing its competitors in performance while remaining reasonably priced.
Key Considerations When Choosing Heat Detection Binoculars
Purpose: Determine the primary application for which you'll be using the binoculars, whether it's surveillance, wildlife observation, hunting, or industrial inspections.
Environmental Conditions: Consider the environmental conditions in which the binoculars will be used, including temperature variations, humidity levels, and exposure to water or dust.
Budget: Set a budget based on your requirements and prioritize features that are essential for your intended application.
Performance: Evaluate factors such as magnification, resolution, field of view, and refresh rate to ensure optimal performance and clarity.
Reviews and Recommendations: Read reviews from experts and users, and seek recommendations from professionals in your field to gain insights into the performance and reliability of different models.
Choosing the right heat detection binoculars entails understanding the differences between thermal and night version technologies. Whether you require precise thermal imaging capabilities or enhanced visibility in low-light conditions, there's a binocular option tailored to your specific needs. By considering factors like purpose, environmental conditions, budget, performance, and expert insights, you can make an informed decision and select heat detection binoculars that offer optimal functionality and reliability.
Guide Sensmart Tech presents a broad spectrum of heat detection binocular products, including the TN430, TN450, TN630 and DN30. Engineered with ergonomic design and user-friendly features, our binoculars deliver swift location and an enhanced observational experience. For unparalleled night vision capabilities, explore our meticulously crafted collection of heat detection binoculars, designed to excel in every scenario.













.svg)

.jpg)